
Polygon


More than 3,000 children are born every year with a congenital limb deficiency in the United States alone. These children will change their prosthetics devices once every 6 months, making the purchase of a high-end prosthesis unaffordable for most families. Affordable 3D printers have spawned numerous customizable and very affordable prosthetic hand models. These devices can be modified to fit the children as they grow, at a relatively low price. However, these prosthetic hands leave a lot to be desired in terms of functionality. Most of these devices can only allow coarse finger control, placing it in stark contrast to commercial automatic hands. The Project Sparthan team is committed to taking the concept of modular prosthetics a step further, continuing to bridge the gap between expensive robotic arms and 3D printed prosthesis. This will be done through the design and development of Sparthan, a modular electronics kit, compatible with existing prosthetic hand models, which will enable intuitive hand control.
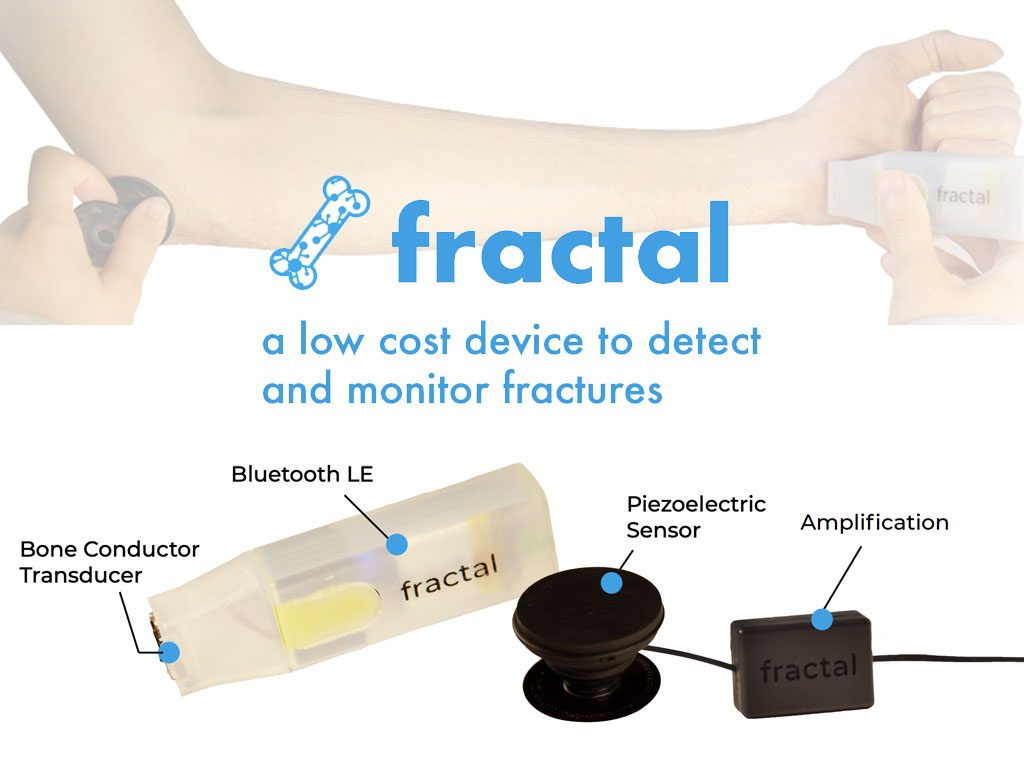
Two-thirds of the world lacks access to basic medical imaging equipment, which is an essential cornerstone for modern medical diagnostics. Due in part to a lack of access to basic x-ray technology in two-thirds of the world, fractures often mean a lifelong disability with devastating socioeconomic complications. In order to mitigate this gap in healthcare, Fractal provides underdeveloped countries and remote settings with an inexpensive, trusted tool for diagnosing and monitoring bone fractures. Fractal sends an acoustic signal through the bone, which is analyzed for sound transmission and frequency changes. The device is currently being tested on patients at the University of California, San Francisco with the aim to facilitate better care and outcomes for patients with plans for further development.
![]()
About 55,000 people in California rely on arsenic contaminated groundwater as their primary source of drinking water. The small water systems serving these disadvantaged communities lack the technical, managerial, and financial capacity to implement a sustainable solution that would provide arsenic-safe drinking water. Thus, there is a need for an affordable, compact, and continuous-flow technology for these communities exposed to arsenic, a potent carcinogen. Air Cathode Assisted Iron Electrocoagulation (ACAIE) effectively removes high arsenic concentrations from synthetic groundwater to levels below EPA’s Maximum Contaminant Level of 10 parts per billion. Conducting a pilot study at a school site will demonstrate the technical efficacy and robustness of ACAIE. In addition, an educational campaign will increase public awareness and knowledge on the arsenic problem in rural California, empowering rural communities that currently lack their human right to safe drinking water.
![]()
Okara is known as a soy pulp by-product generated when processing soy-based products. While okara still contains high nutrition values, most of it is dumped into landfills where it creates greenhouse gas emissions, causing environmental concerns. Okaranchi crackers aims to alleviate the global food waste issue by introducing consumers to a nutritious, sustainable and innovative snacking alternative. This appetite-fulfilling cracker is gluten-free, rich in protein and fiber, and low in high-glycemic carbohydrates, all of which meet conscious consumers’ concerns when making food purchases. Okaranchi can be consumed as its own snack, eaten as a crunchy component in soup and salad, or paired with dippings, spreads, nut butter, and even fruit, cheese, and wine. Through appealing and informative packaging, a sustainability-focused vision, and education outreach, consumers will realize that they are doing good to both their bodies and the environment through their purchase of Okaranchi.
![]()
Billions of pounds of polyethylene are produced each year, and unfortunately this compound can take thousands of years to break down. Polyethylene has also been linked to human cancers, groundwater toxification, and environmental damage. A reliable means of breaking down polyethylene is necessary and would have a huge impact. Unfortunately, microbial degradation of polyethylene is not common in nature. Polyethylene has been around for less than 100 years and enzyme evolution takes millennia, so microbes have not had enough time to develop this ability. However, recent techniques in Directed Evolution allow researchers to take evolution into the lab and speed it up to thousands of times its natural rate. This project proposes to apply Directed Evolution techniques to a specific enzyme tied to polyethylene degradation in order to create a novel enzyme capable of degrading polyethylene efficiently and reducing global plastic waste.
![]()
Improving Women’s Lives with Improved Cookstoves in Rural India
The ultimate goal of the Berkeley India Stove (BIS) Project is to deliver the BIS into the hands of the poorest 830 million people in India suffering from exposure to indoor air pollution due to their daily use of inefficient biomass cookstoves. An essential component of the project is to ensure the sustained adoption and long-term usage of the BIS, which reduces smoke emissions and fuelwood consumption by as much as 50% compared to traditional Indian stoves. The BIS is one of the best available cookstoves in the Indian market considering a performance to price ratio. Bolstered by strong partnerships on the ground and a comprehensive business plan, including innovative strategies for dissemination and monitoring, the BIS has the potential to dramatically curtail the harmful impacts of this critical environmental, health, and socioeconomic issue caused by inefficient stoves.
![]()
60% of Americans are suffering from chronic diseases, of which 80% are preventable by a healthy lifestyle. With all of the current options available for health and wellness, we still aren’t preventing disease. Why? The current options are prescriptive, focused on one or two areas of health, and lack a sense of camaraderie and accountability. Enter Viva: a solution to shape the future of preventative health. Viva community centers empower urban women to reduce chronic stress and gain self-awareness through holistic health lifestyle management. Viva’s tech-enabled wellness clubs offer holistic health & wellness education, online and offline resources and community-building to help shift mindsets and create sustainable behavior change. Viva is providing a personalized, accessible and social way to find the lifestyle that makes you the healthiest and happiest version of yourself.

At first sight, people begin to form judgements about each other in their heads based on appearance, race, gender, and other superficial factors. These are called “implicit biases”, and they affect the ways we think, act, and perceive the world around us. From gender discrimination in the workplace to racial profiling in our communities, many of the issues we face as a country stem from the consequences of our implicit biases. Seminar is a platform intended to be used in the high school classroom to address these biases in an engaging and unique manner. Through a mobile app, students are allowed to converse with their peers through a model that facilitates productive conversations without the inhibitions of superficial influences. Through proprietary pairing and impact algorithms, Seminar learns about the community it is deployed in and improves the student experience over time.